 |
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Epub ahead of print |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Notes
FUNDING
This research was supported by the Technology Innovation Program, A Platform for Prediction and Management of Health Risk Based on Personal Big Data and Life-logging, funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (grant no., 200002781) and the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry through the High Value-Added Food Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (grant no., 321030051HD030).
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Figure.┬Ā1.

Figure.┬Ā2.
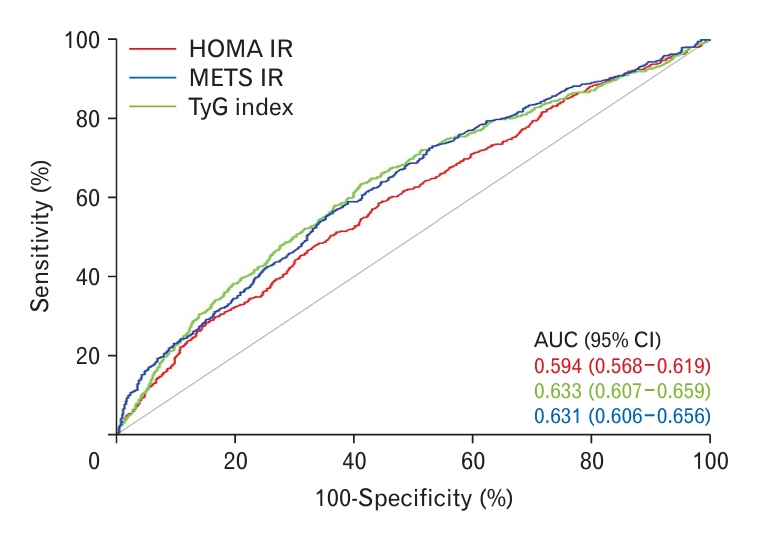
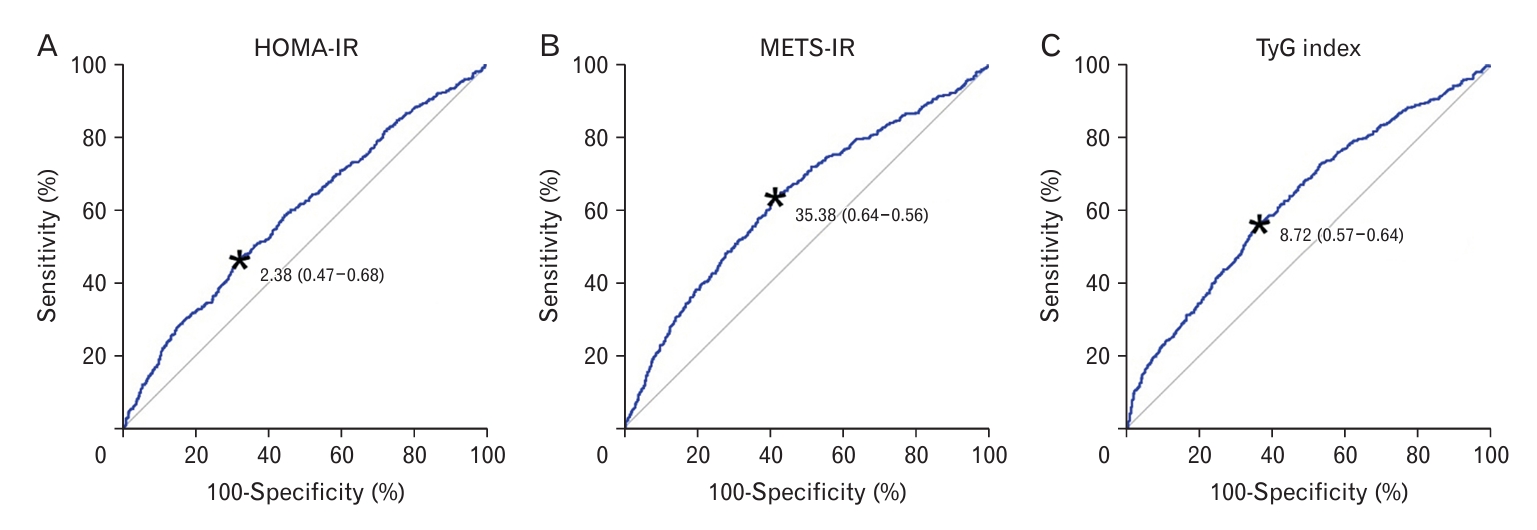
Figure.┬Ā3.
Table┬Ā1.
Values are presented as number (%) or mean┬▒standard deviation. Categorical and continuous variables were calculated using the weighted chi-square test and weighted two-sample t-test, respectively.
HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; METS-IR, metabolic score for insulin resistance.
Table┬Ā2.
Model 1: adjusted for sex and age; model 2: adjusted for model 1 plus socioeconomic factors (such as household income, educational level, aerobic exercise, restricted activity, smoking status, and alcohol consumption); and model 3: adjusted for model 2 plus diseases (such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and obesity).
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; Ref, reference; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; METS-IR, metabolic score for insulin resistance; TyG, triglyceride-glucose.
Table┬Ā3.
| Variable | AUC (95% CI) | Overall P-value |
Post-hoc P-value* |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOMA-IR | METS-IR | TyG index | |||
| IR index | <0.001 | ||||
| ŌĆāHOMA-IR | 0.594 (0.568ŌĆō0.619) | Ref | |||
| ŌĆāMETS-IR | 0.633 (0.607ŌĆō0.659) | 0.002 | Ref | ||
| ŌĆāTyG index | 0.631 (0.606ŌĆō0.656) | 0.004 | 0.910 | Ref | |
REFERENCES
- TOOLS







