|
 |
- Search
| Korean J Fam Med > Volume 33(1); 2012 > Article |
Abstract
Background
While smoking prevalence in Korean men has been decreasing, it is increasing in Korean women. Little is known about women's smoking inequalities in Korea. This study was conducted to investigate the association of socioeconomic indicators with the initiation and cessation of smoking among Korean women.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study on 9,089 women aged 25-64 years from the 2008 Seoul Community Health Survey. The data on smoking and socioeconomic status were obtained through face-to-face interviews. Smoking initiation rate was defined as the proportion of the individuals who had started smoking at least one cigarette among all subjects. Smoking cessation rate was calculated by dividing the number of individuals who had quit smoking by the number of ever smokers. Education level, total family income and occupation were investigated as socioeconomic indicators.
Results
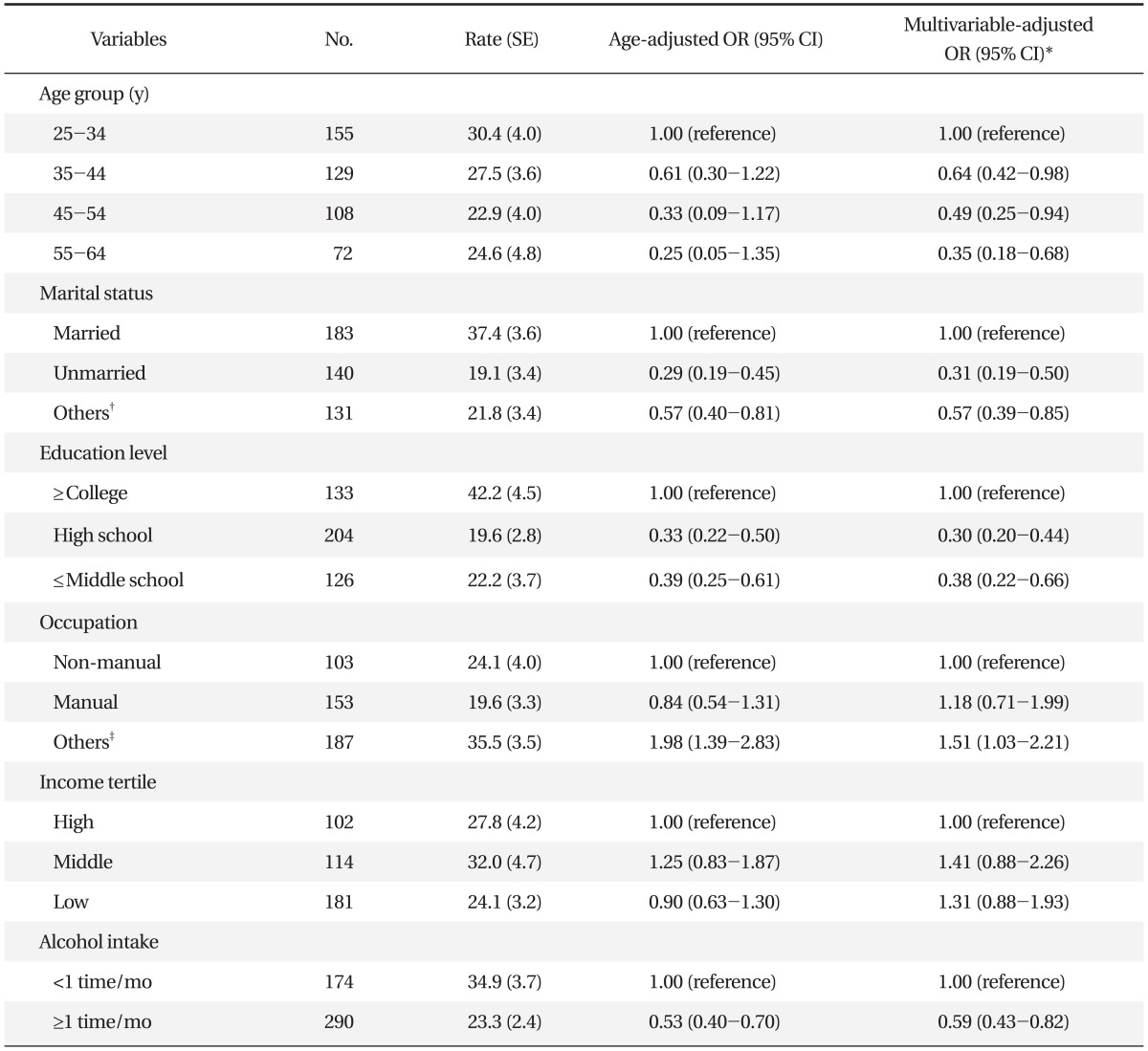
Education level was significantly associated with both initiation and cessation of smoking. Lower educated women had a higher likelihood of smoking initiation (odds ratio [OR], 1.72; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.17 to 2.51) but lower likelihood of smoking cessation (OR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.22 to 0.66) than higher educated women. Smoking initiation rate was higher in manual workers (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.20 to 2.27) than in non-manual workers. However, there were no significant differences of both initiation and cessation of smoking according to total household income.
Smoking is a major cause of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases and premature death.1,2) The increase of these smoking-related illnesses and deaths has lead to increased national socioeconomic burden via the increase of medical care costs and the loss of labor productivity.3) With increased awareness of the harmful effects of smoking on both individuals and society, intense tobacco control policies such as the increase of cigarette tax and the expansion of no-smoking areas have been implemented in Korea.4) These tobacco control policies has been effective on reducing men's smoking.5) However, women's smoking prevalence has increased.6)
The harmful health effects of smoking might be more serious in women than in men. Female smokers are more susceptible to lung cancer than male smokers7) and face additional health risks for female-specific diseases like cervical cancer, infertility and premature menopause. In addition, smoking during pregnancy can cause serious pregnancy complications such as low-birth weight, ectopic pregnancy and spontaneous abortion.8)
Health behaviors including smoking are different depending on socioeconomic status (SES) factors like education level, income level or occupation. Kim9) examined the socioeconomic inequalities and their trends in smoking prevalence with data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) in 1998, 2001, and 2005. They reported that education level and total family income were inversely associated with smoking prevalence and the SES gradient in smoking worsened over time, especially in men aged 25-64 years. The current smoking status is the net result of various processes of initiation, maintenance and cessation of smoking.10) It can be considered that the inequalities in current smoking comprise inequalities in smoking initiation and cessation. However, there are few studies on the inequalities in smoking initiation and cessation in Korea. Kim et al.11) recently reported that several socioeconomic indicators were related to smoking initiation or cessation in Korean men from KNHANES 2005. However, they excluded women in their study because smoking in women was not frequent enough to study. Studies in other countries have also described socioeconomic inequalities in the initiation and cessation of smoking in women.12-15)
This study was conducted to investigate the association of socioeconomic indicators with initiating and cessation of smoking among women aged 25-64 years from the 2008 Seoul Community Health Survey (CHS).
The data of women who participated in 2008 Seoul CHS were used. The survey methodology has been previously detailed.16) The survey was performed between September and November 2009 and the target population of the survey was anyone ≥19-years-of-age residing in Seoul during the survey period. The trained interviewers visited the samples of households and conducted face-to-face interviews on all adults in the households. Total participants of the survey were 21,928 individuals. Among them, 9,096 individuals were women aged 25-64 years. Seven women who did not answer any smoking questions were excluded from the present study. Finally, the data of 9,089 women were available for the final analyses.
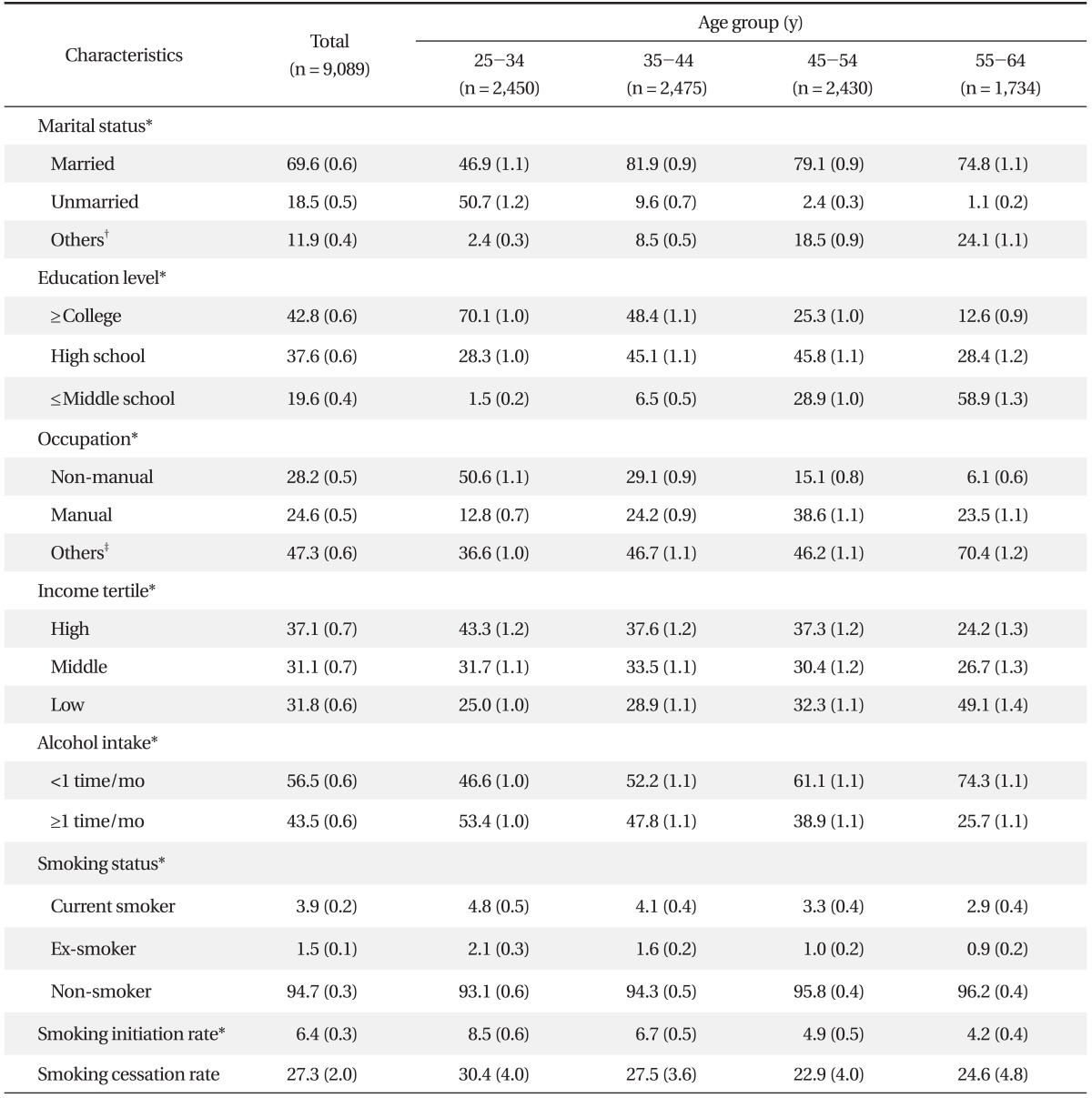
Study subjects were classified into ever smokers if they reported that they had smoked at least 100 cigarettes during their lifetime and non-smokers if they reported that they had never smoked or had smoked fewer than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime. Ever smokers were subclassified into current smokers, who currently smoked, and ex-smokers, who did not currently smoke. Smoking initiation rate was defined as the proportion of the individuals who had started smoking at least one cigarette among the total study subjects. Smoking cessation rate was calculated by dividing the number of individuals who had quit smoking by the number of ever smokers.
Education level, total family income and occupation were investigated as socioeconomic indicators. Education level was classified as less than or achievement of graduation of middle school, graduation from high school and more than or achievement of graduation of college. For economic status, household equivalent income was calculated by dividing total family income by the square root of the number of family members. The calculated household equivalent income was categorized as tertiles (high, middle, and low). Occupation was classified into three occupational groups of non-manual workers, manual workers and the others by the Korean Standard Classification of Occupation revised in 2007. While 1) managers, 2) professionals and related workers, 3) clerks were included in non-manual workers, 4) service workers, 5) sales workers, 6) skilled agricultural, forestry and fishery workers, 7) craft and related trade workers, 8) equipment, machine operating and assembling workers, and 9) elementary workers were included in manual workers. Additionally, soldiers, students, homemakers, and unemployed were classified as others. Marital status was categorized into three groups: married, unmarried, and others (divorced, separated, or widowed). Drinking status was classified into two groups by frequency of alcohol intake: <1 time a month or ≥1 time a month.
Every analysis was performed by taking into account sample weights, stratification and primary sampling units from CHS. Data were expressed as percentage ± standard error. Logistic regression analyses were used to obtain odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of each socioeconomic indicators on initiation and cessation of smoking. There was likely no problem concerning multicollinearity because all values of the variance inflation factor for independent variables in the regression models were <2.0. All statistical analyses were performed with PASW ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and P-values < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The mean age of the study subjects was 42.2 ± 1.1 years (range, 25 to 64 years). Sociodemographic characteristics of the study subjects with smoking status are shown in Table 1. The initiation rate and the cessation rate of smoking in total subjects were 6.4 ± 0.3% and 27.3 ± 2.0%, respectively. Both smoking initiation and cessation rate was highest in 25-34 age group.
OR and 95% CI of each socioeconomic indicator on smoking initiation are presented in Table 2. Compared to women who graduated from college, women who did not graduate from college had a higher likelihood of smoking initiation (high school: OR, 1.35, 95% CI, 1.04 to 1.75; ≤middle school: OR, 1.72, 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.51). Smoking initiation was significantly higher in women who had manual jobs (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.20 to 2.27) or other jobs (OR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.87) than in women who had non-manual jobs. Age-adjusted OR of the low income group (1.74; 95% CI, 1.35 to 2.24) compared to the high income group was statistically significant. However, significance was not apparent following adjustment by marital status, alcohol intake, education level and occupation. Smoking initiation rate was higher in younger women and unmarried, divorced, separated and widowed women. Smoking initiation rate in women whose frequency of alcohol intake was ≥1 time/mo was more than twice as great as women whose frequency of alcohol intake was <1 time/mo.
Data on OR and 95% CI of each socioeconomic indicators on smoking cessation are presented in Table 3. Compared to women who graduated from college, women who did not graduate from college had a lower likelihood of smoking cessation (high school: OR, 0.30, 95% CI, 0.20 to 0.44; ≤middle school: OR, 0.38, 95% CI, 0.22 to 0.66). Smoking cessation rate was not significantly different between manual workers and non-manual workers, but was higher in women who had other jobs (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.03 to 2.21) than in women who had non-manual jobs. There was not a significant relationship between household income level and smoking cessation. The smoking cessation rate was higher in younger women and married women. Smoking cessation rate in women whose frequency of alcohol intake was <1 time/month was about 1.7-times higher than that in women whose frequency of alcohol intake was ≥1 time/month.
This study aimed to investigate the socioeconomic inequalities in initiation and cessation of smoking among women aged 25-64 years using data from the 2008 Seoul CHS. Lower educated women had a higher smoking initiation rate and lower smoking cessation rate and women who were employed at manual labor had the highest smoking initiation rate. These results suggest that there are remarkable socioeconomic inequalities in the initiation and cessation of smoking among Korean women, similar to reports from other countries.12-15)
Generally, smoking among females was popular longer ago in developed countries, and has been more recently increasing in Asian countries including Korea.7) Women's smoking prevalence may reflect the extent to which their country's culture accepts smoking by women. As women's rights have been extended and women's role in society has expanded, the smoking prevalence in women has increased. Smoking by women has become more accepted and popular. Young women are used to social activities that are apt to expose them to smoking and can be more open-minded about smoking. These cultural transitions may be driving the increasing prevalence of smoking in women despite the intense tobacco control policies in Korea. Even though the harmful effects of maternal smoking in pregnancy are well-known, many women report smoking during pregnancy.17) However, there have been few studies on women's smoking in Korea.
This study shows that women's education level is closely related with both the initiation and cessation of smoking. Education level has been the most frequently studied smoking indicator among the various socioeconomic indicators.18) Higher educated subjects are less likely to be current smokers, since they are less likely to begin smoking and are more likely to be successful in smoking cessation.18-20) Leinsalu et al.12) reported that educational level was the strongest predictor of the initiation of regular smoking in both men and women. Schaap et al.20) reported that higher educated smokers are more likely to have quit smoking than lower educated smokers in all age-sex groups in European countries. Higher educated subjects, who are generally more health-conscious, seem to be more responsive to messages about the harmful effects of smoking on health than lower educated subjects. Therefore, anti-smoking campaigns which more effective in higher educated subjects could increase educational inequalities in smoking.14,21)
Presently, the smoking initiation rate was higher in workers employed in manual labor than in non-manual workers. Occupation-related differences of smoking behavior could be a result of job-specific toxic environmental exposures or different socioeconomic position reflected in each occupation.22) Next to education level, occupation is the most frequently using socioeconomic indicator; more prestigious jobs are related to lower smoking rate in western developed countries.18) Cho et al.22) reported that non-manual labor was related to higher smoking rate among Korean men and smoking rate in service workers was the highest especially among Korean women. A Finnish study23) showed smoking was more prevalent among subjects whose parents had manual jobs throughout a follow-up from adolescence to adulthood. This result suggests that smoking in lower socioeconomic classes could extend from one generation to the next.10,18) In this study, the smoking cessation rate was the highest among women who had other jobs. This finding may have reflected the inclusion of homemakers in other jobs.
Whereas Kim et al.11) reported household income was related to smoking cessation in Korean men, there was no relationship of household income with initiation and cessation of smoking in Korean women. These results are consistent with the previous report of a significant relationship of household income with smoking cessation in men, but the lack of a relationship between household income with initiation or cessation of smoking in women.12) It is likely that income itself does not directly affect health, but instead have an effect on heath via the conversion of income into health enhancing commodities and services.24) Although smoking prevalence is generally lower in those with a higher income than those with a lower income,25) this relationship is not remarkable compared to the relationship of education level or occupation with smoking prevalence.18) Further research is needed to evaluate the effects of household income on women's smoking.
An increasing trend of smoking prevalence among young women including teenagers from 1992-2006 prompted the prediction that smoking prevalence in Korean women would continue to increase.26) However, the present data revealed high likelihood of smoking initiation and cessation in younger Korean women. The results imply that prevention of smoking initiation and encouragement of smoking cessation focusing on young women can be effective in curbing the increasing trend of the smoking prevalence among Korean women over time. Development of anti-smoking policies that are effective for young women should be a national public health priority.
This study had several limitations to be considered. Some socioeconomic indicators cannot sufficiently reflect women's social classes. The classification of women's occupation is not clear concerning full-time homemakers. Additionally, SES can affect health behaviors in different ways between working women and full-time homemakers.27) The definition of smoking initiation varies among studies. As well, the study suffered from the limitations inherent to a cross-sectional study.
Despite these few limitations, the present data is meaningful in that the socioeconomic inequalities in initiation and cessation of smoking among Korean women are revealed for the first time.
In conclusion, the present study documents socioeconomic inequalities in the initiation and cessation of smoking among Korean women. Lower educated women have a higher likelihood of smoking initiation and a lower likelihood of smoking cessation than higher educated women, and the smoking initiation rate of women engaged in manual labor is higher than non-manual workers. Furthermore, education level and occupation are likely important determinants of women's smoking status.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control (CDC). The surgeon general's 1989 report on reducing the health consequences of smoking: 25 years of progress. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1989;38(Suppl 2):1-32.

2. Song HR, Kim CH. Epidemiology of the smoking-related diseases in Korea. J Korean Acad Fam Med 2008;29:563-571.
3. Kim SJ, Kwon SM. The social cost of smoking in Korea. Korean J Policy Anal Eval 2008;18:119-140.
4. Seo HG, Cheong YS, Myung SK, Kim Y, Lee WB, Fong GT. Smoking-related characteristics in Korean adult smokers: findings from the 2005 International Tobacco Control Policy Evaluation Survey-Korea. J Korean Acad Fam Med 2008;29:844-853.
5. Korean Ministry of health and Welfare. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008. 2008. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
6. Seo MK. Women's smoking behavior and its implications. Health Welf Policy Forum 2009;152:73-82.
7. Jung JJ. Why do we need the smoking cessation control for the women? 2010;In: Korean Women Smoking Cessation Forum; 2010 May 31; Seoul, Korea. Seoul, Korean Association of Smoking and Health.
9. Kim HR. Socioeconomic inequality and its trends in cigarette smoking in South Korea, 1998-2005. Health Soc Welf Rev 2007;27:25-43.

10. Gilman SE, Abrams DB, Buka SL. Socioeconomic status over the life course and stages of cigarette use: initiation, regular use, and cessation. J Epidemiol Community Health 2003;57:802-808. PMID: 14573586.



11. Kim SR, Kim OK, Yun KE, Khang YH, Cho HJ. Socioeconomic factors associated with initiating and quitting cigarette smoking among Korean men. Korean J Fam Med 2009;30:415-425.

12. Leinsalu M, Tekkel M, Kunst AE. Social determinants of ever initiating smoking differ from those of quitting a cross-sectional study in Estonia. Eur J Public Health 2007;17:572-578. PMID: 17403786.


13. Legleye S, Khlat M, Beck F, Peretti-Watel P. Widening inequalities in smoking initiation and cessation patterns: a cohort and gender analysis in France. Drug Alcohol Depend 2011;117:233-241. PMID: 21420251.


14. Federico B, Costa G, Kunst AE. Educational inequalities in initiation, cessation, and prevalence of smoking among 3 Italian birth cohorts. Am J Public Health 2007;97:838-845. PMID: 16809593.



15. Fernandez E, Garcia M, Schiaffino A, Borras JM, Nebot M, Segura A. Smoking initiation and cessation by gender and educational level in Catalonia, Spain. Prev Med 2001;32:218-223. PMID: 11277678.


16. Seoul Metropolitan Government. Community heath survey report, Seoul, 2008. 2009. Seoul: Seoul Metropolitan Government.
17. Kong SH, Kim SY, Lee HJ, Kim HS, Lee DW, Kim JY. The clinical study on the neonate delivered under the condition of the maternal smoking and alcohol in pregnancy. Korean J Pediatr 2005;48:34-39.
. Lee JE. Health inequalities in South Korea: cigarette smoking behavior among social class between 1995 and 2001 [dissertation]. 2005. Seoul: Seoul National University Graduate School of Sociology; Korean
19. Borrell C, Rue M, Pasarín MI, Rohlfs I, Ferrando J, Fernandez E. Trends in social class inequalities in health status, health-related behaviors, and health services utilization in a Southern European urban area (1983-1994). Prev Med 2000;31:691-701. PMID: 11133336.


20. Schaap MM, Kunst AE, Leinsalu M, Regidor E, Ekholm O, Dzurova D, et al. Effect of nationwide tobacco control policies on smoking cessation in high and low educated groups in 18 European countries. Tob Control 2008;17:248-255. PMID: 18483129.


21. Fernandez E, Schiaffino A, Garcia M, Borras JM. Widening social inequalities in smoking cessation in Spain, 1987-1997. J Epidemiol Community Health 2001;55:729-730. PMID: 11553656.



22. Cho HJ, Khang YH, Yun SC. Occupational differentials in cigarette smoking in South Korea: findings from the 2003 Social Statistics Survey. J Prev Med Public Health 2006;39:365-370. PMID: 16910312.

23. Huurre T, Aro H, Rahkonen O. Well-being and health behaviour by parental socioeconomic status: a follow-up study of adolescents aged 16 until age 32 years. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2003;38:249-255. PMID: 12719840.


24. Galobardes B, Shaw M, Lawlor DA, Lynch JW, Davey Smith G. Indicators of socioeconomic position (part 1). J Epidemiol Community Health 2006;60:7-12. PMID: 16361448.


25. Cho HJ, Song YM, Smith GD, Ebrahim S. Trends in socioeconomic differentials in cigarette smoking behaviour between 1990 and 1998: a large prospective study in Korean men. Public Health 2004;118:553-558. PMID: 15530934.


26. Seo MK, Choi EJ, Kim DJ, Park SW. Factors related to women's smoking and drinking behavior and policy plan. 2008. Seoul: Korean Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
27. Choi YJ, Jeong BG, Cho SI, Jung-Choi K, Jang SN, Kang M, et al. A review on socioeconomic position indicators in health inequality research. J Prev Med Public Health 2007;40:475-486. PMID: 18063903.


- TOOLS